in
linux
software
If you are using Linux, you can easily install TeamViewer and use it to connect to remote machines that are also running TeamViewer be it Windows, Mac OS X, or Linux.
Installing TeamViewer:
Using TeamViewer:
Keep Reading
How to Install and Use TeamViewer on Linux
TeamViewer is one of the most popular remote desktop software because it is really easy to use and it has support for different operating systems. Although its main function is to remote control a desktop for technical support, it also has file sharing and presentation features.
If you are using Linux, you can easily install TeamViewer and use it to connect to remote machines that are also running TeamViewer be it Windows, Mac OS X, or Linux.
Installing TeamViewer:
The full version of TeamViewer for Linux has packages for several major distributions, such as Debian, Red Hat, Fedora, Mandriva, Suse, and Ubuntu. You can download them from HERE. So if you are using any of the supported distros, simply install TeamViewer using the package manager.
Using TeamViewer:
When you run TeamViewer, make sure that it is also running on the remote (partner) machine that you would like to control or connect to, and close it only after you have ended your session. You can immediately connect by getting and entering your partner's ID and password.

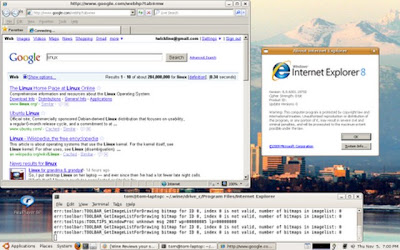
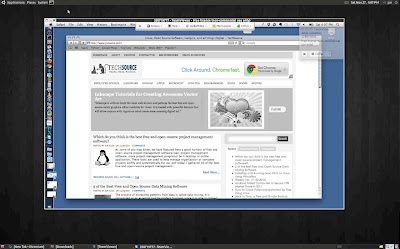
Here is a screenshot of TeamViewer on my Linux desktop remote controlling a Mac OS X machine:

That's how easy it is to install and use TeamViewer on Linux. If you want to remote control your Linux desktop using the iPhone, see this post: Remote Control Your Linux Desktop Using the iPhone.